In the dynamic digital landscape, spam threats have emerged as a clandestine threat to WordPress websites, subtly targeting their internal search functionalities. In this article, I will shed more light on this sneaky technique and provide valuable insights on safeguarding your site’s SEO and brand integrity.
In many cases, SEO’s due to daily job tasks, are the first to flag a spam attack. As a common scenario, Google Search Console will offer SEOs the first hint to guide them and indicate that something is wrong with their website.
The first question that comes to mind is how you identify such internal search spam attacks.
Any WordPress website has two types of search urls as a result of a website search query:
yourwebsite.com/?s=example and yourwebsite.com/search/example/
If you use the Yoast SEO plugin on your WordPress website, you must know that it adds a robot’s “noindex”, and “follow” tag to URLs generated by internal searches.
You’ll probably think that you are covered but the question is: Is this “noindex” robots tag enough to keep your website protected against such types of internal search spam attacks?
It is, but it’s just half of the job you need to get done in order to be 100% protected and your website to stay healthy.
Let’s dig deeper into this spam technique first
Internal search spam attacks involve unethical practices aiming to manipulate a website’s use of a third-party website to get some results or do harm to the attacked website. Exploiting WordPress sites’ internal search features to craft pages promoting illegal or inappropriate goods and services.
Exploiting Internal Search Functionality
Attackers utilize the internal search functionality of WordPress sites to generate pages with advertisements for illicit goods or services. Though these pages might not immediately damage your site’s SEO, they set a precarious stage that could lead to significant problems if not promptly addressed.
Potential Consequences for Brands and SEO
If search engines index these spam-generated pages, it might not only tarnish your brand’s online reputation but also harm your website’s SEO. When these URLs get associated with low-quality spam sites, the situation escalates, dragging your site’s ranking down with them.
Proactive Prevention Measures for WordPress website owners and admins
Preventing the indexing of these spam-infested pages is crucial. WordPress owners or admins must meticulously manage their SEO settings, ensuring these unwanted pages remain not indexed, thereby safeguarding both brand image and SEO performance.
Using Yoast SEO is the first step you can take against internal search spam attacks
Yoast automatically appends a “noindex” “follow” robots tag to your site’s internal search results pages, effectively preventing search engines from indexing these potentially harmful pages.
The exploitation of internal search functionality is a nuanced tactic that might seem harmless initially but can have cascading negative effects in the long run for your website rankings.
In this case, additional steps and actions need to be taken in order to consider that such spam attacks are not going to harm your website rankings in the long run.
A “noindex” robots tag on a page on your website still does not fixes the risk of having rankings affected. We know that all these search pages return 200 OK (success) HTTP status codes.
200 OK – Google passes on the content to the indexing pipeline. The indexing systems may index the content, but that’s not guaranteed.
So, the crawling step by Googlebot has been completed even though there is a “noindex” robots tag in place.
404 Not found error – An effective approach?
We know from Google search central documentation on crawling and indexing content that: “Google’s indexing pipeline doesn’t consider URLs that return a 4xx status code for indexing, and URLs that are already indexed and return a 4xx status code are removed from the index.”
Considering the above definition of 404 not found status code pages, it’s still not clear if managing to return 404 Not found pages for those internal search spam attacks is a better option than 200 OK.
Back in 2018, Google’s John Mueller made an interesting statement on Google Webmaster Central office-hours hangout, about 404 not-found pages:
“404 pages do not need to be blocked from crawling (for the purpose of preserving the crawl budget). You will not lose crawl capacity from 404 crawls.”
Crawl Budget from Small to big websites – How it Plays out in a Internal Search Spam Attack
Considering the huge amount of search pages created over an internal search spam attack, “crawl budget” could be negatively impacted. Crawl budget refers to a limited number of pages Googlebot will crawl on your website within a certain timeframe.
Google is trying to answer to many questions about this topic over time and a good starting point is an official article published back in 2017 here:
One of the factors affecting the crawl budget is the low quality and spam content.
“Wasting server resources on pages like these will drain crawl activity from pages that do actually have value, which may cause a significant delay in discovering great content on a site.”
Considering the above statement definitely, we should agree that hundreds of spam, low-quality pages that are generated through an internal search spam attack will affect your website crawl budget.
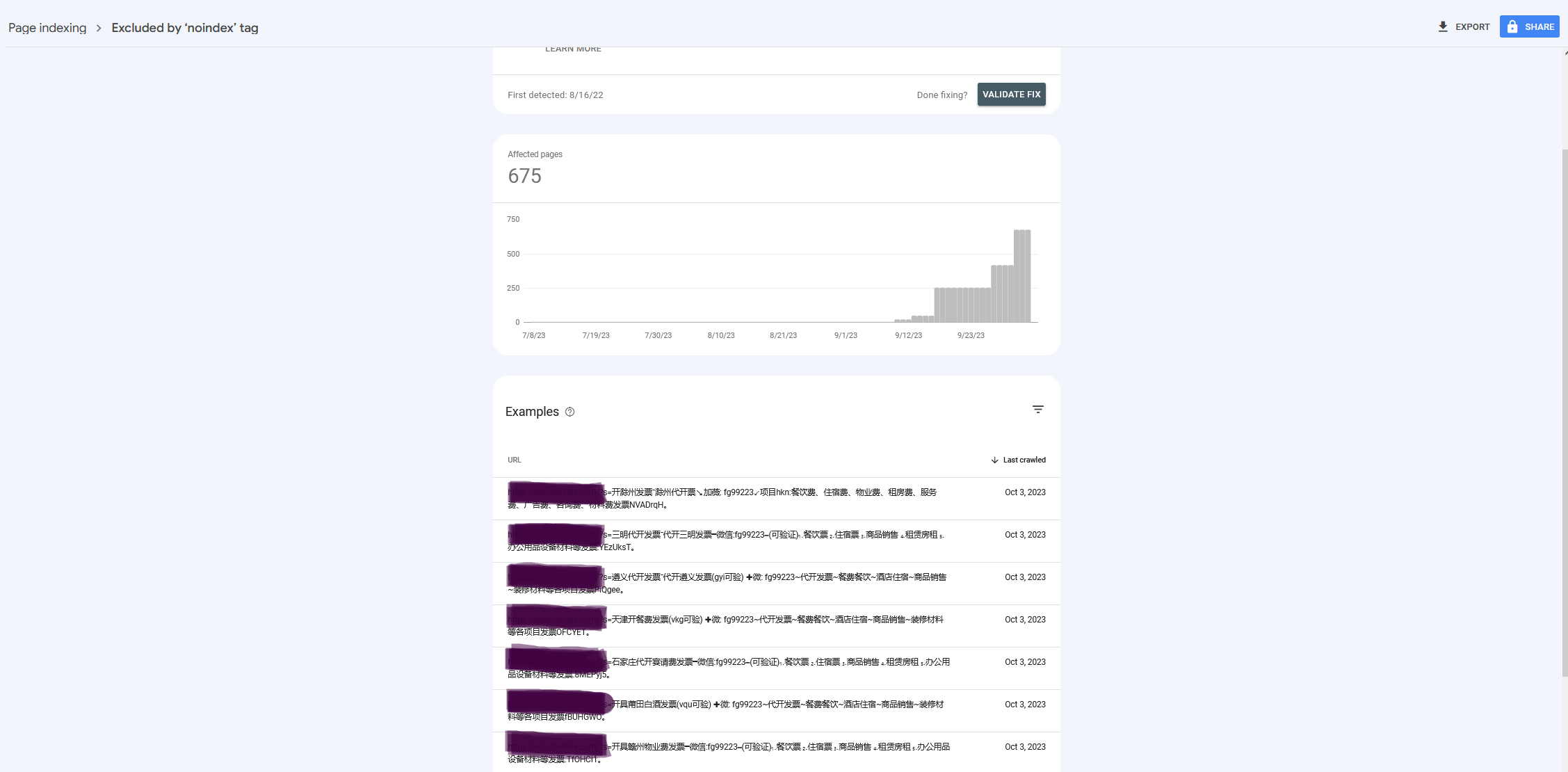
Internal Search Spam Attack – Case Study
We recently had a case where in a few days 600+ new search pages have been generated with a rate of 200+ pages per day in an internal search spam attack. Our client’s ecommerce website is not on WordPress but the content section is created under a WP CMS.
As you can see from the screenshot below, search urls that include Chinese characters are reported on GSC and considered excluded using a “noindex” tag added automatically by the Yoast SEO plugin.
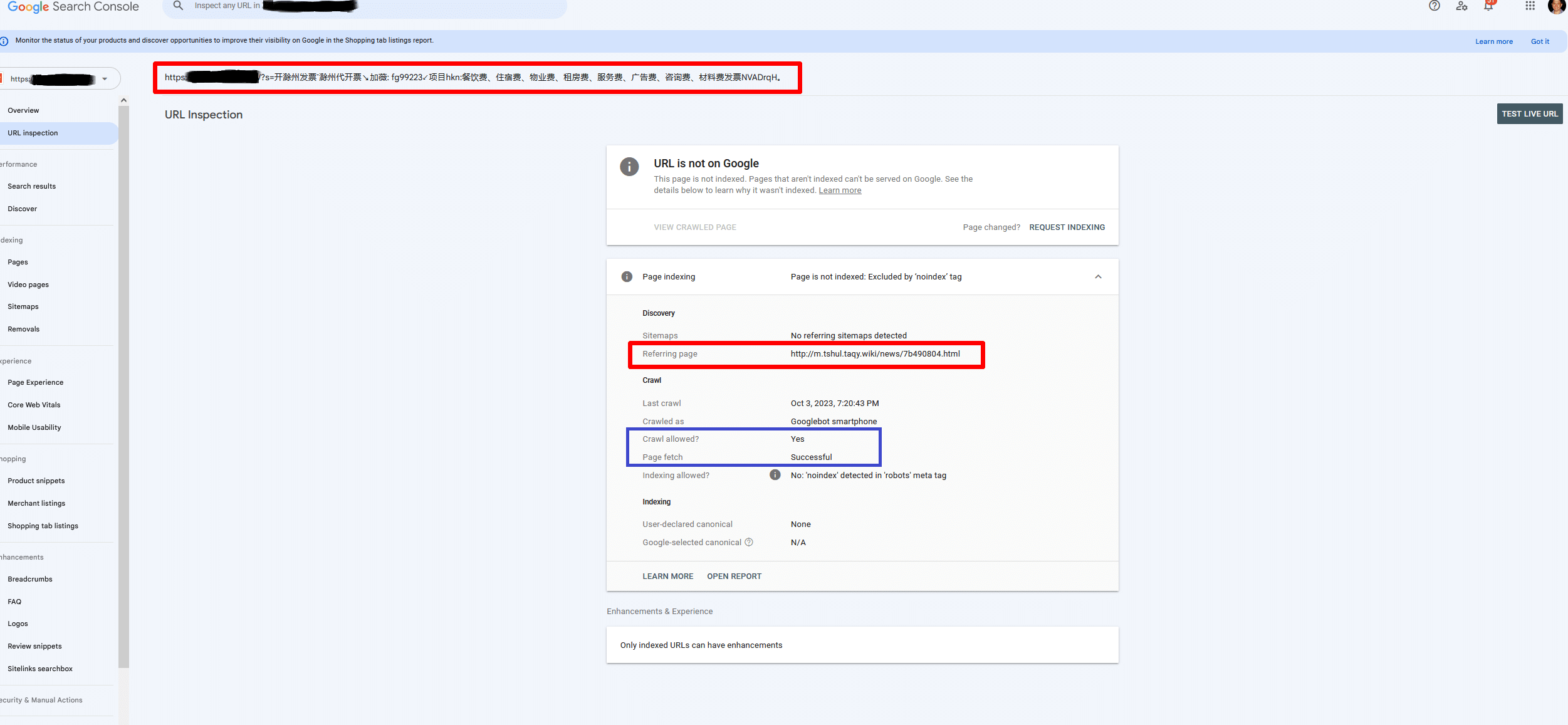
We started to dig deeper into these spam search urls and we noticed that there was a quite sophisticated attack using sort of non-existing referral subdomains created at scale to deploy such spam attack.
A good resource on disabling the internal search on WordPress we found here
There are two options, the plugin option and the manual option though code added to functions.php file.
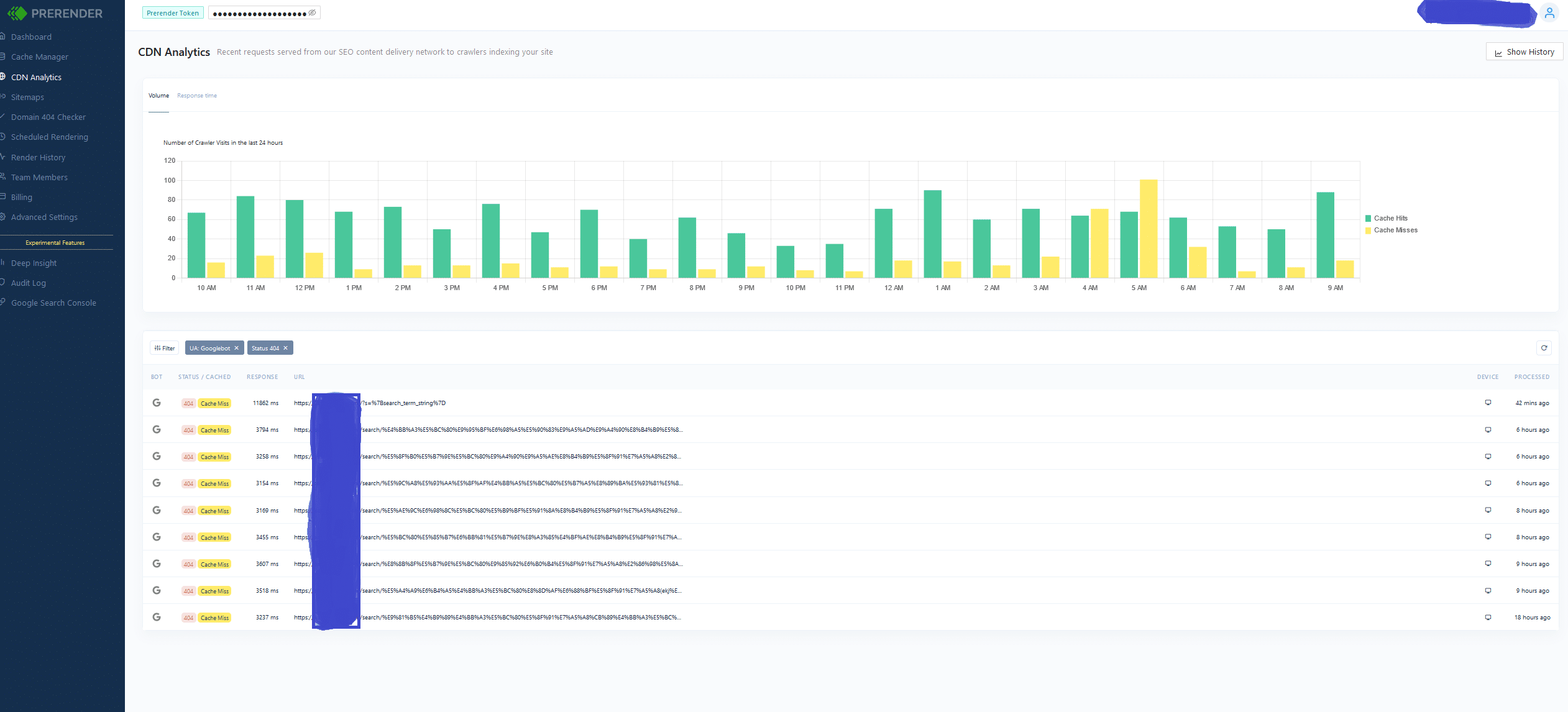
Even in big companies, you’ll find situations where on a Friday afternoon nobody will be available to deploy some code on a production WordPress website. So, installing and releasing a WordPress plugin it was the quickest yet most effective temporary solution. We closely monitored the internal search spam attack and after disabling the search functionality the number of new 404 error pages generated has been significantly reduced.
Final Thoughts
Internal search spam attacks on WordPress websites could generate thousands of low-quality and spam content pages in days. So, taking quick measures is key when the SEO segment is essential for your business health.
Monitor your website closely and use different tools to keep a closer eye on every key point of your website:
- How many “not indexed” pages does your website have vs “indexed” pages?
- How many are excluded by the “noindex” tag page your website has?
- How many “not found” 404 error pages have your website?
Another insightful statistic from the Google search console is: “Crawled – currently not indexed”.
Identify the reasons you notice spikes on these key points and find solutions to reduce the number of these pages. Search for resources on the matter and make the connection between your case and other similar described and fixed cases.
I’m looking forward to having your thoughts on how you fixed internal search spam attacks.


